Google Position Checker In Three Simple Steps

Achieving a high Google positions is very important to every business owner. If you check out the following photo, you’ll see a strong correlation between CTR and position.

I don't know about you, but I don’t check Google rankings for the specific keywords because I think results are becoming more and more personal, so here’s what I do.
I check average rankings in Google Search Console which tells me how well my SEO efforts are. In this blog post, I’ll show you how to check Google rankings in three simple steps:
- Add and verify a property
- Open Search Traffic - Search Analytics
- Export rankings to Google Sheets
Furthermore, I’ll discuss other tools that you can use for checking the rankings.
Let’s explore them!
Step #1: Add And Verify A Property
Your first step is having a verified Google Search Console property. So, open the tool, and click on ADD A PROPERTY button.

Keep in mind that the following URLs are two completely different properties:
- https://www.jellymetrics.com
- http://jellymetrics.com
This also tells us that you always need to use 301 redirects because Google treats different www and non-www versions of the site.
If you don’t implement 301 redirects, you’ll have a duplicate content which is not good.
The next step is verifying ownership of the site. For this, there are so many methods and here are some of them:
- Recommended method
- Alternate methods

Recommended method is using Google Tag Manager which I’d recommend too because GTM will help you when you need to implement other tools and things like that.
As for alternate methods, here’s what you can do:
- Upload an HTML file to your site
- Add a meta tag to your site’s home page
- Sign in to your domain provider
- Use your Google Analytics account

As I said, I always verify a page through Google Tag Manager, and I recommend you to do that too.
Once you verify the property, you should see the following message.

After you click on Continue your dashboard should look like this.
 Now, let’s see how to find rankings.
Now, let’s see how to find rankings.
Step #2: Search Traffic - Search Analytics
In the menu, click on Search Traffic - Search Analytics.

Take a look at the following photo and you’ll see four metrics:
- Clicks
- Impressions
- CTR
- Position

Clicks tell you how many clicks your site had in the past period and impression number tells you how many times your site appeared in the search results.
Impressions metric is always good to see your SEO trends. Take a look at the following photo and see how great this metric is.

Next, CTR is the result from dividing Clicks and Impressions.
Here’s the formula.

Finally, Position is what you are looking for, so you need to tick its checkbox.
Additionally, you can increase the number of dates up to 90 days.

Now I want to explain how does Position metric work. It’s actually an average position where your site appeared.
If one query returned your site at positions 5 and 24, your position for that query is counted as 5 (top position will be counted).
Next, if another query returned your site at positions 6, 14, 26, your position is counted as 6.
Now, simple math says that an average position for the example above will be exactly 5.5
AVG. POSITION = (5 + 6) / 2 = 5.5
Search Analytics is not only about the total average position because there you can see average positions for:
- Queries you rank
- Pages you rank
- Countries where you rank
- Devices you rank
- Search type you rank
Now, I want to show you how it looks when you sort top pages by the number of clicks and also when you display average positions.

This is awesome because this way you know which pages have the highest search volume and a solid position which means you can find enough space for improvements.
If you don’t know why this screenshot has Monthly Volume column, and you don’t see that in your Google Search Console column, here’s the answer.
You have to install Keywords Everywhere extension which will add search volume, CPC, and competition data to all your favorite websites:
- Ubersuggest
- Soovle
- Answer The Public
- Majestic Anchors
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Keyword Shitter
- Moz Open Site Explorer

Next, you can also see search analytics grouped by countries.

Thanks to this, I know that this site has better rankings in the UK than the United States, but it has more visits from the United States.
Also, checking the positions for mobile devices seems very important because we know that mobile responsivity is important Google ranking factor.

If your site doesn’t rank well for mobile devices, you should check if your site is mobile-ready.
One of the most popular tools for checking mobile responsivity and generally, checking if something is wrong with your site is Google PageSpeed Insights.
Here are some potential errors your mobile version may have.

Now, let’s see how to analyze the data in Google Sheets.
Step #3: Export Rankings To Google Sheets
Checking the position directly in Google Search Console is fine, but if you want to analyze it better, you’d definitely need to export the data to Google Sheets.
The process is very simple. Firstly, scroll down and click on DOWNLOAD button.

There, you need to select download format, and there are two options:
- CSV
- Google Docs
Of course, you’ll pick Google Docs and click on OK. 
Immediately, you’ll download a CSV file which you need to import in Google Sheets which is unquestionably trivial.
In the menu, click on File - Import...

There, a modal dialog will appear and you actually have four different tabs:
- My Drive
- Shared with me
- Recent
- Upload
Of course, you’ll pick the last tab (Upload) and drag a file you downloaded a couple of seconds before.

When importing, you’ll have few options, but I always pick Replace spreadsheet and click on Import.

Keep in mind that this will replace a spreadsheet so you always need to open a blank (new) spreadsheet. You’re almost done.
For a better overview, you should freeze the first row by clicking on View - Freeze - 1 row.

Now, you’ll see lots of queries that you rank for, but I’d always suggest you finding long-tail keywords.
You probably know that achieving high for rankings for long-long tail keywords is a lot easier than ranking short-tail keywords.
If you don’t know what long-tail keyword is, let me say that every phrase that contains more than 4 words is actually long-tail keywords.

What's more, your goal is probably to increase the number of conversions, and what’s good about long-tail keywords is that they are more commercial because the intent is more specific.
Take a look at the following photo and you’ll see how to count total words.

This is the formula: =COUNTA(SPLIT(A2, " "))
Once you enter the formula for the first row, just apply it to all the words, and you’ll have something like this.
 That’s it.
That’s it.
This means that you’ll be able to find long-tail keywords that have a solid number of impressions, but a low number of clicks and low position.
With a few internal links, you should be able to improve the rankings for those terms. This way, you’ll increase the traffic of your blog.
EXTRA CHAPTER: Which Other Tools You Can Use?
Checking rankings in Google Search Console is only one way, and there are so many other free and paid tools that make you checking positions possible. Here’re some of them.
#1 Allorank
This tool lets you free check how does your domain rank for the specific keyword.
For example, you can enter jellymetrics.com as your domain, how to find long-tail keywords as the phrase, and click on Start: get my position.

The results will appear within a second.

Unfortunately, I haven’t found an API that would let me check rankings programmatically which is definitely a con.
#2 SERPs Keyword Rank Checker
This tool allows you check rankings both for Google and Yahoo.
In the input fields enter free CRM software and hubspot.com. I know that HubSpot has a great free online CRM software, so I’m sure the tool is on the first page of Google.

So, just click on Go. I was right.
HubSpot ranks on the position number three which is great for this term.
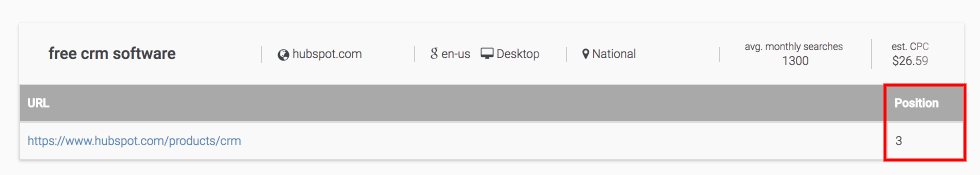
Furthermore, you can get rankings for desktop and mobile devices which is always good because mobile results are adjusted to mobile users (responsivity e.g.).
#3 Search Engine Reports
For this tool, you can also enter hubspot.com in the specify domain field, and free CRM software in the field intended for keywords.
This tool checks positions up to 50 pages, but unfortunately, you can add only 5 keywords per request. So, add keywords and click on Check Search Ranking.

The results are the same - third position which tells us that both these tools are accurate.

For example, if that’s not the case, it would mean that there’s some problem with results.
Unfortunately, the tool doesn't offer an API so you’ll need to enter keywords manually or buy some paid tool which would let you do that.
Conclusion
Just as I said, I don’t track rankings for specific keywords, but I track average rankings in Google Search Console because it tells me how well my SEO is.
Using Search Analytics in Google Search Console will surely help you to generate lots of new long-tail keywords that have a good potential.
For example, maybe you rank on 3rd or 4h page for some term which has really high search volume, so with a couple of content changes and internal links, you might rank on the first page.
These three tools I mentioned in the extra chapter was for manually checking the rankings.
For example, you don’t want to open incognito mode and check ranks when you can do it in these tools with a couple of seconds.
