#1 Brevo
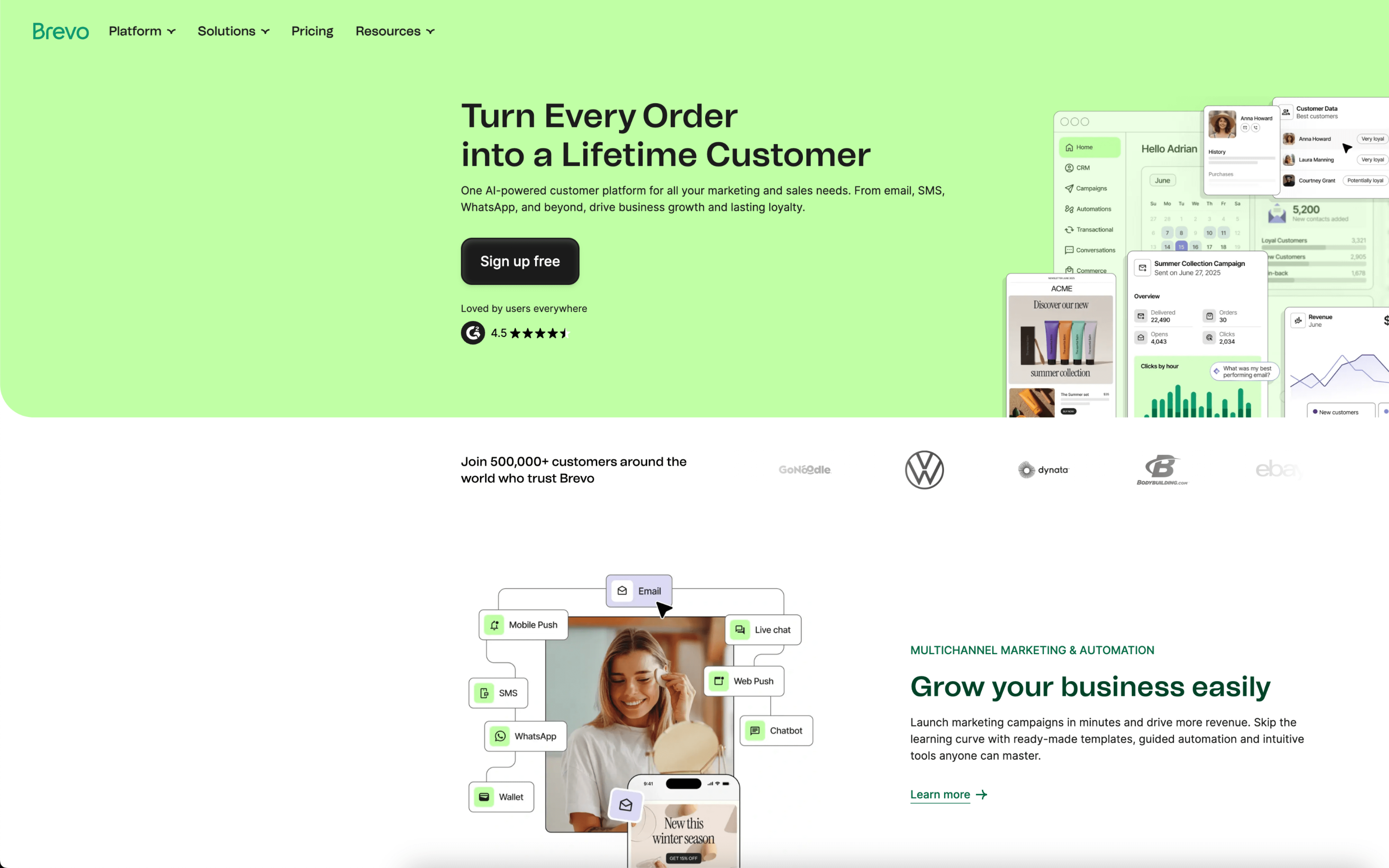
Brevo is used by teams that manage customer communications across email and SMS alongside a shared contact database. It commonly shows up in organizations that need both marketing campaigns and system-driven messages tied to customer activity.
Teams import and maintain contacts, organize them into lists or segments, and then run a mix of scheduled campaigns and trigger-based automations. Day to day, marketers draft and QA messages, while operations or product teams connect forms, ecommerce events, or APIs so customer actions update segments and start workflows.
Good Fit For
- Teams sending weekly or monthly newsletters while also running automated onboarding, re-engagement, or post-purchase sequences
- Organizations that need marketing email and transactional notifications coordinated from the same contact record and reporting view
- Teams coordinating basic sales follow-up by assigning tasks and tracking contact activity alongside campaign execution
Considerations
- Getting consistent segmentation and automation often requires careful data hygiene and agreement on how contacts, attributes, and lists are managed across teams
- Some workflows depend on integrations or API-driven data updates, which can add implementation effort and ongoing monitoring