#1 Klaviyo
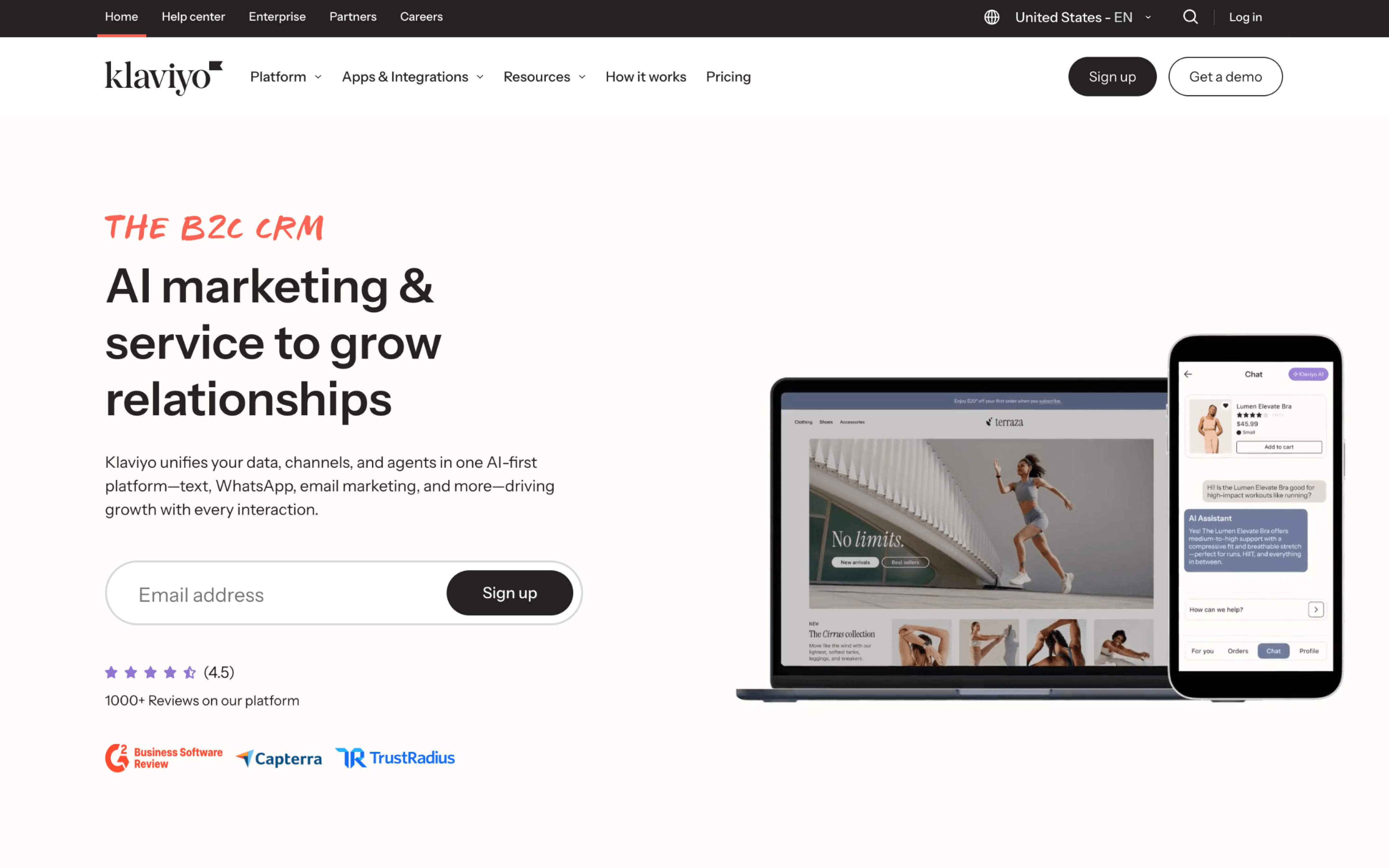
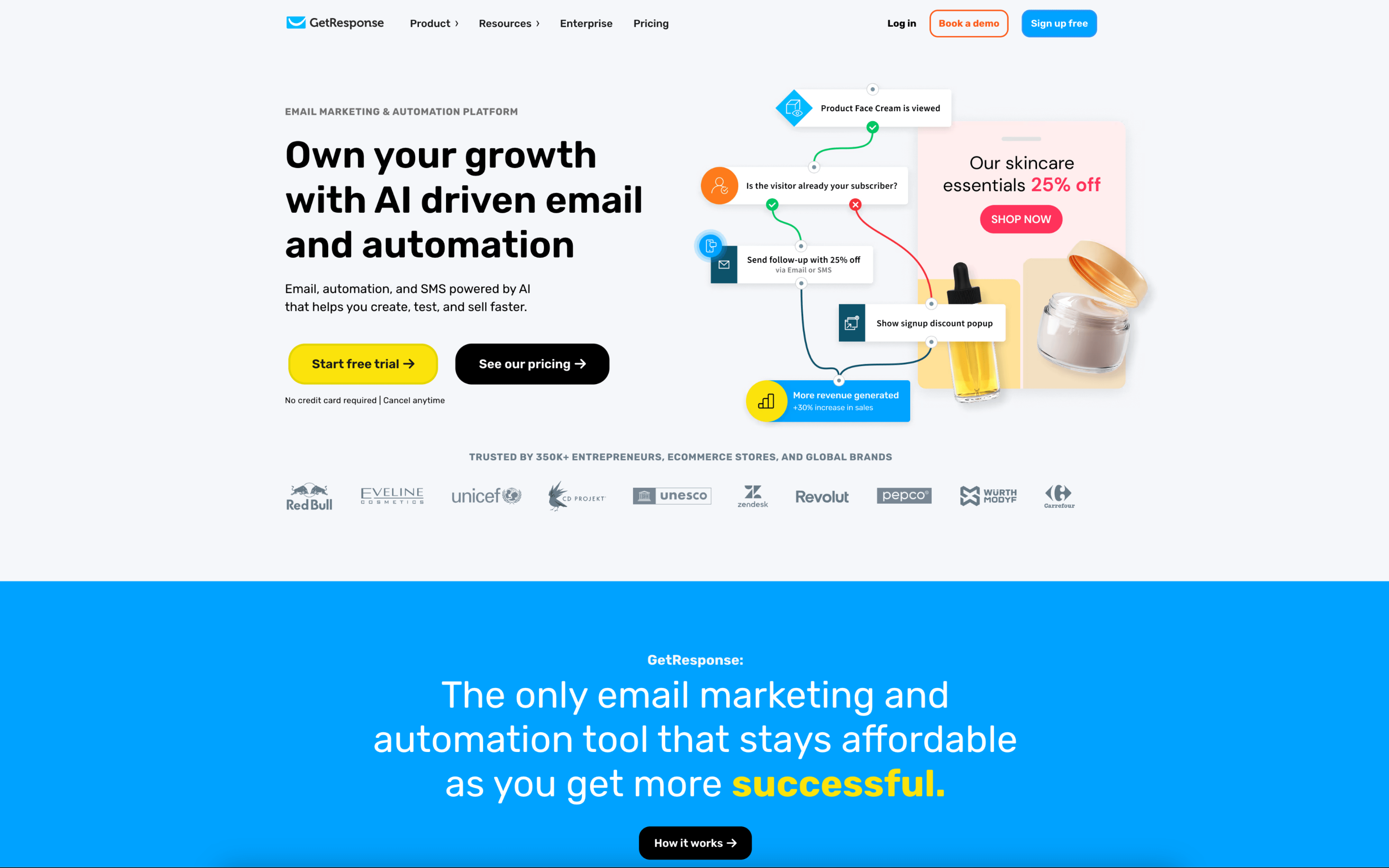
Klaviyo is typically used by B2C and ecommerce marketing teams that run customer lifecycle messaging based on shopping and engagement behavior. It is often operated by marketers who want to build targeted outreach without relying on a large technical team.
Teams connect their store and data sources, then organize audiences around events like browsing, cart activity, purchases, and predicted value. Work often splits between recurring broadcasts and always-on lifecycle flows, with regular review of segment logic, timing, and performance reporting.
Good Fit For
- Ecommerce teams running weekly promotional sends alongside automated welcome, cart abandonment, and post-purchase sequences
- Marketing teams that segment audiences using combined purchase history and onsite behavior, then tailor messaging by intent or value
- Teams coordinating cross-channel outreach where the same campaign is planned as a timed sequence across multiple message types
Considerations
- Maintaining clean event tracking and consistent naming becomes ongoing operational work as segments and flows grow
- Cross-channel cadence can be harder to govern as more triggers are added, increasing the risk of message overlap without careful coordination