#1 ActiveCampaign
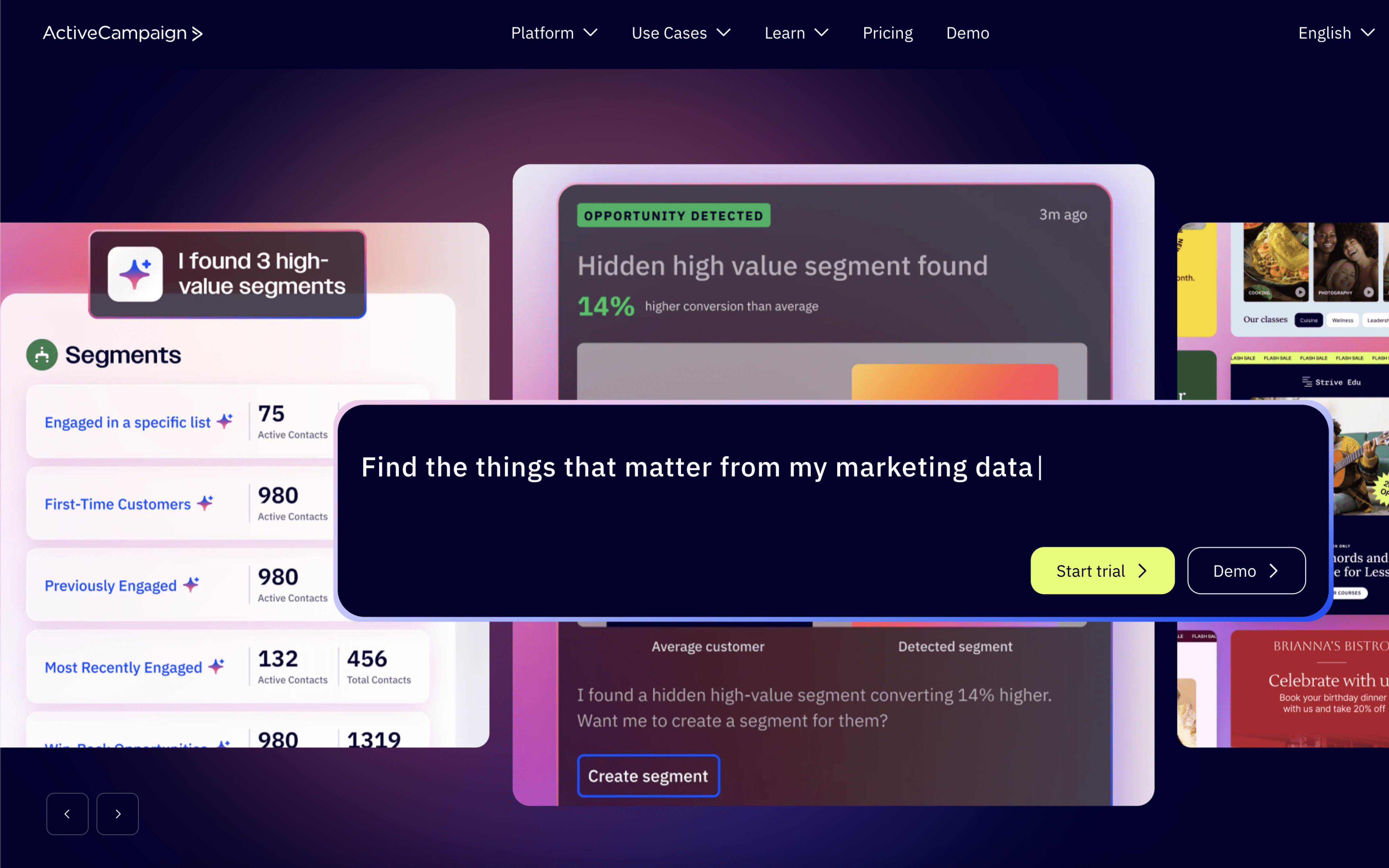
ActiveCampaign is typically used by small to mid-sized marketing and sales teams that want one place to run lifecycle messaging while tracking leads and deal progress. It often sits with a growth marketer, sales lead, or operations generalist who maintains automations and data hygiene.
Teams usually import contacts, connect website and app integrations, then build segments that update as people take actions. Day to day, they monitor automations that trigger emails and follow-ups, route leads into a pipeline, assign tasks, and review engagement to adjust campaign timing and handoffs.
Good Fit For
- Teams running recurring newsletters and promotional sends alongside always-on onboarding or nurture sequences
- Organizations that need marketing-triggered deal creation, pipeline stage updates, and rep task assignment tied to contact behavior
- Workflows where a small team coordinates campaign launches weekly while maintaining automated follow-ups continuously
Considerations
- Combining campaign work, automations, and CRM-style pipelines in one workspace can require ongoing governance to keep naming, segmentation, and routing rules consistent
- Behavior-based journeys depend on accurate tracking and integrations, so setup and troubleshooting can become a regular operational task